59710409H3BK Fundamental Photographs The Art of Science

Mudstone an extremely finegrained sedimentary rock consisting of a mixture of clay and silt
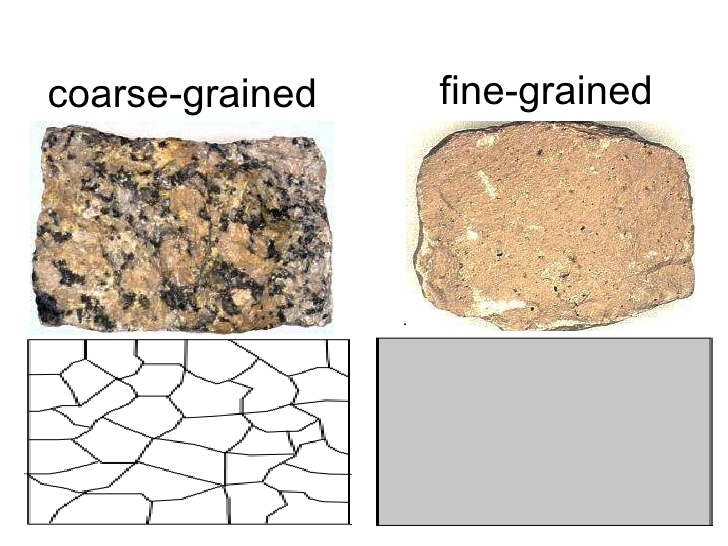
Grain Size. Detrital rock is classified according to sediment grain size, which is graded from large to small on the Wentworth scale (see figure).Grain size is the average diameter of sediment fragments in sediment or rock. Grain sizes are delineated using a logbase-2 scale [9; 10].For example, the grain sizes in the pebble class are 2.52, 1.26, 0.63, 0.32, 0.16, and 0.08 inches, which.
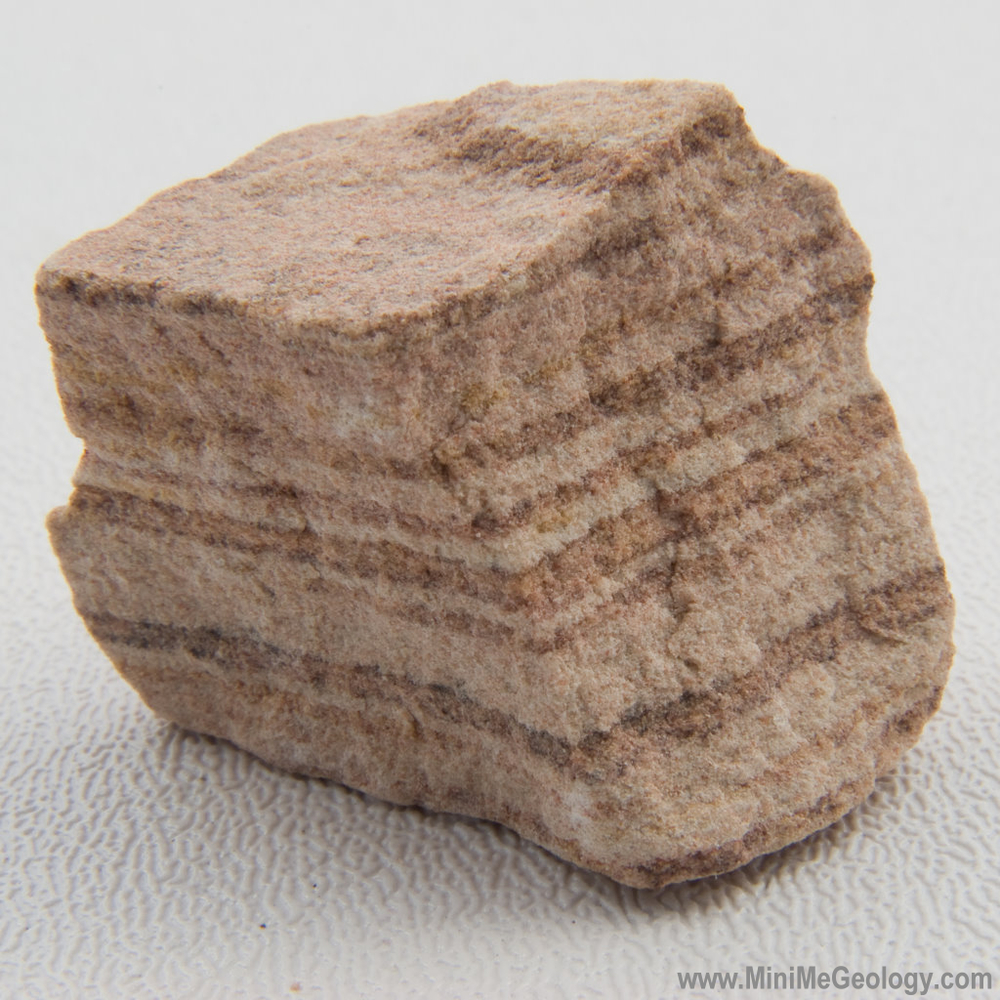

Banded Sandstone Sedimentary Rock Mini Me Geology
Chert ( / ˈtʃɜːrt /) is a hard, fine-grained sedimentary rock composed of microcrystalline or cryptocrystalline quartz, [1] the mineral form of silicon dioxide (SiO 2 ). [2] Chert is characteristically of biological origin, but may also occur inorganically as a chemical precipitate or a diagenetic replacement, as in petrified wood. [3]

Texture and Structure of Sedimentary Rocks Forestry Bloq
fine-grained sedimentary rock rock classification three-level nomenclature particle size mineral composition RESEARCH PAPER PETROLEUM EXPLORATION AND DEVELOPMENT Volume 49, Issue 1, February 2022 Online English edition of the Chinese language journal Cite this article as: PETROL. EXPLOR. DEVELOP., 2022, 49 (1): 121â€"132.

Sedimentary structures in the very fine grained sandstone host rock.... Download Scientific
In the present work, the thermal conductivity of fine-grained sedimentary rocks, sampled from boreholes and outcrops, was analysed in laboratory scale. Thermal conductivity of the examined rocks ranges from 0.96 to 6.06 W m −1 K −1. The measured parameter is strongly dependent on the composition of mineral assemblage and bedding direction.

59710409H3BK Fundamental Photographs The Art of Science
Classifications of fine-grained sediments and sedimentary rocks are based on combinations of several criteria. These include: (1) texture, (2) fissility, (3) tectonic association or environment of deposition, (4) mineral composition, (5) color, (6) chemical composition and (7) degree of metamorphism.

SR2bHow to Observe, Identify, and Name Common, Coarsegrained, Clastic Sedimentary Rock YouTube
The Crossword Solver found 30 answers to "Fine grained sedimentary rock", 5 letters crossword clue. The Crossword Solver finds answers to classic crosswords and cryptic crossword puzzles. Enter the length or pattern for better results. Click the answer to find similar crossword clues . Enter a Crossword Clue Sort by Length # of Letters or Pattern
Granularity — Strong Towns
Despite their abundance, fine-grained sedimentary rocks, to date, have not been satisfactorily classified. Perhaps this is because they are not well exposed in the field compared to their coarser.

Finegrained Rock Surface Detail Stock Image Image of material, textured 110550435
shale, any of a group of fine-grained, laminated sedimentary rocks consisting of silt- and clay-sized particles. Shale is the most abundant of the sedimentary rocks, accounting for roughly 70 percent of this rock type in the crust of the Earth. Shales are often found with layers of sandstone or limestone.

Slate Stone is a Finegrained, Foliated, Homogeneous Metamorphic Rock Derived from an Original
In this paper, therefore, we present major and trace element geochemical data of the fine-grained sedimentary rocks (i.e., siltstones and shales) from the Ikorongo basin. The purpose of the study is to constrain source(s) of the Ikorongo clastic sedimentary rocks and to understand the weathering conditions in the source region(s). 2.

Grain Size. Detrital rock is classified according to sediment grain size, which is graded from large to small on the Wentworth scale (see figure).Grain size is the average diameter of sediment fragments in sediment or rock. Grain sizes are delineated using a logbase-2 scale [9; 10].For example, the grain sizes in the pebble class are 2.52, 1.26, 0.63, 0.32, 0.16, and 0.08 inches, which.

Shale Stone is a Finegrained, Clastic Sedimentary Rock Composed of Mud that is a Mix of
Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\): Image of the classic Bouma sequence. A=coarse- to fine-grained sandstone, possibly with an erosive base. B=laminated medium- to fine-grained sandstone.. , also called up-direction indicators, are used to identify which way was up when the sedimentary rock layers were originally formed. This is especially important.
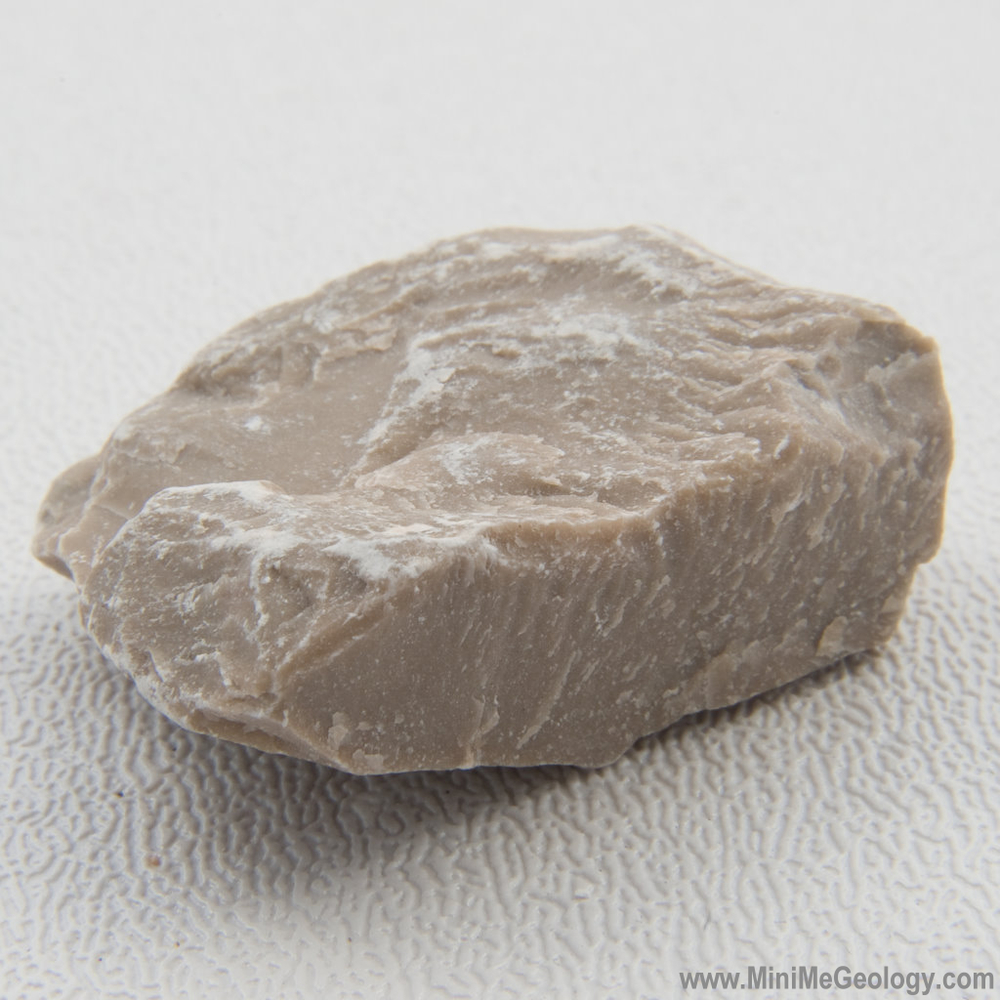

Limestone Sedimentary Rock Mini Me Geology
A fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock, composed of mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especially quartz. Shale is characterized by breaks along parallel layering or bedding less than one centimeter in thickness, called fissility. It is the most common sedimentary rock.

Shale is a finegrained, clastic sedimentary rock composed of mud that is a mix of flakes of
The lithofacies classification of fine-grained sedimentary rocks is an important basis for the study of hydrocarbon source rocks, shale oil and gas and tight oil reservoirs.

Brown Oil Shale Sedimentary Rock 10 Raw Pieces Sedimentary rocks, Sedimentary, Oil shale
What is Shale? Shale is a fine-grained sedimentary rock that forms from the compaction of silt and clay-size mineral particles that we commonly call "mud." This composition places shale in a category of sedimentary rocks known as " mudstones ." Shale is distinguished from other mudstones because it is fissile and laminated.

59710409G3BK Fundamental Photographs The Art of Science
Shale is a fine-grained, sedimentary rock composed primarily of clay and silt-sized particles. It is characterized by its thin layers or bedding planes, often making it easily fissile and enabling.

SR2dHow to Observe, Identify, and Name Common Finegrained Sedimentary Rock YouTube
Fine-grained sediments and sedimentary rocks ("Mudrocks") Mud is a general term lumping together sediments consisting of a mix of clay, silt, and may contain sand. Mud is usually an unsorted mix of fine grain materials. Mud accumulates in quiet water settings separated from where coarser materials have settled out elsewhere (Figure 6.46).